Intruduction
Nursing education is a profession that is planned and carried out in a thoughtful and methodical manner through instruction and discipline. Nursing education comprises specific training programs for working nurses as well as post secondary education programs like bachelor's and master's degrees. The beliefs and viewpoints that healthcare practitioners should have in order to improve patient and facility outcomes are another focus of nursing education.1
Education is a beacon that points humanity in the proper way as it progresses. The goal of education is to develop a student's reasoning skills, general knowledge, and sense of independence. While innovation is the process of constructive thinking, organizing knowledge, abilities, and attitude into new, creative, and rational ideas, critical thinking is the important component in delivering safe, competent and skillful nursing practice.
Bachelor’s and master’ s degree programs in nursing as well as specific training courses for working nurse are all included in post secondary nursing education. In order to improve patient and facility outcomes, nursing education also emphasizes the values and attitudes that health care practitioners should have.
Education is a beacon that directs people toward the right path for development. Literacy, critical thinking, general knowledge, and a sense of independence are all skills that should be developed in students as part of their education. While critical thinking is a necessary part of delivering safe, competent, and skillful nursing practice, innovation is the process of constructive thinking, organizing information, talents, and attitude into new, creative, and logical ideas. For nurses to be prepared to work in a variety of contexts, innovation in nursing education is necessary.2
Experiential Learning Theory
Kolb’s experiential learning theory
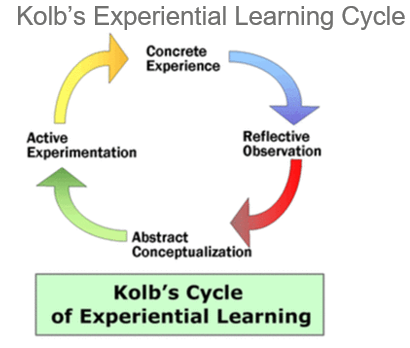
David Kolb became well-known for his contributions to the experiential learning theory, or ELT. Kolb published this paradigm in 1984, taking cues from a number of eminent theorists like Kurt Lewin, Jean Piaget, and John Dewey. Active exploration, abstract conceptualization, reflective observation, and concrete learning are the four stages of the experiential learning theory. The first two stages of the cycle are about taking in an experience, while the final two are about changing an event. According to Kolb, as the learner progresses through the cycle, it will become clear whether or not they are actually learning anything.3, 4
Experiential Learning Model
"Do Reflect Decide" is the fundamental cycle of experience learning.
Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory presents a cycle of four elements.
Kolb described two different ways of grasping experience:
He also identified two ways of transforming experience:
Experiential Learning Cycle: Four Stages
Concrete experience
The practical experiences from which we learn are referred to as concrete experience. Here, we take risks, confront challenges, and push ourselves past our comfort zones. Any encounter from our personal or professional lives could qualify as one of these. We only learn from our achievements or failures via experience.
Reflective observation
After that, we must ponder in order to draw lessons from our past.
The' reflective observation' stage of the experiential learning cycle is all about reflection on the experiences, which encompass both action and feelings. We think back on the experiences at this point. We have the opportunity to consider what went well and what could be improved. Additionally, it's a time for everyone to learn from one another and consider how it might have been done differently.
For Nursing Students, the Benefits of Experimental Learning Include
The capacity to instantly put information to use
Experiential learning gives students the chance to use what they've learned to address problems in the real world. Learners can experiment and modify their practice to get the greatest results by testing their comprehension of the underlying principles, methods, and procedures.
Having access to coaching and feedback in real-time
Practice and focused coaching based on what is seen during practice are necessary for achieving expertise. Every experiential learning activity should be followed by a debriefing session where participants get advice and support from subject matter experts and other team members.
Encouragement of communication and teamwork
The majority of medical mistakes are caused by a lack of teamwork and communication. We should study and practice in teams because patient care is given by a team.
Establishing reflective practice practices
The person who can self-monitor the success of his strategy, foresee consequences, and create backup plans is the gold standard in education. These persons are frequently referred to as "experts." They are experts because they have more experiences and coaching than a non-expert and because they regularly apply specific thinking disciplines. The transition from a novice to an expert can be sped up by experiential learning.
Accomplishment are obvious
Becauseof the feedback loop generated by problem-solving, receiving feedback, and practicing again, learners can advance and recognize their advancement in as little as an hour. In a traditional classroom, students frequently don't know whether they are on the right track untilthey sit for an exam and receive their score.
The syllabus distributed to nursing students on the first day of class comprised the outcome objectives and integration recommendations.
Implications of experiential learning for educators.
Learning experiences can be created in accordance with the selected learning style when participants' (and your instructors') learning preferences are known.
Teachers can create learning experiences that are emotionally compelling, immersive, and more closely related to real world applications by using both Kolb's learning styles and the experiential learning model.
Teachers must make sure that the experiential learning activities are planned and = executed in such a way that each student has the opportunity to participate in the way that best matches their preferred learning methods.
Combining learning styles with the learning cycle enables educators to tailor more specialized learning sessions for the participants, supporting participants to learn more effectively and efficiently.
Teachers can create learning activities that relate to the learning intervention in accordance with Kolb's four stages, taking into account how participants process information.
By offering several learning opportunities, we boost the likelihood that the learner will properly assimilate the material and assist them acquire insights that would otherwise be beyond their capacity if the learning had taken place in a different style. To create a well rounded learning experience in a real world setting, activities and learning experiences should be designed in a way that builds upon each step of the experiential learning cycle and takes the participants through the entire process in sequence.7
Strategies used in nursing as an experiential learning
Project based Learning
Case based learning
Inquiry based learning
Clinical experience
Pros and cons Grid
Cross-age peer tutoring
Student teaching
Study abroad
Making mnemonic
Field trip activities
In service learning
Volunteering
Fishbowl
Apprenticeship
Prodigy
Fellowships
Internship
Practicums
Undergraduate research
Simulations and gaming /role playing
Cooperative ( work or community based ) learning
Laboratory ,workshop or studio work
Student Generated test questions.
Application areas of experiential learning
Team Building
Team bonding
Trust building
Collaboration
Communication
Motivating teams
Assertiveness
Decision making
Innovation
Strategic thinking
Creativity
Customer Focus
Confidence building
Conflict management
Management development
Leadership development programs
Coaching
Mentoring
Stress management
Emotional intelligence 7
Conclusion
The increasingly complex role of a nurse requires a much higher level of critical thinking and clinical judgment skills than in the past. Opportunities to provide critical thinking experiences in clinical settings are challenged by various factors, including limited clinical facilities and a shortage of nurse faculty. Alternative methods to provide critical thinking experiences in undergraduate nursing education are required. Kolb's theory of experiential learning theory is discussed as the foundation for the development of an alternative strategy that uses moderate-fidelity manikins. The strategy involved scenario-based performance of selected nursing skills in order to evaluate critical thinking and theory-clinical correlation.