Introduction
Biographic information
Health History
Table 1
Demographic data
Type of family
Nuclear
Persoal History
Life style habits and beliefs: Ex-smoker and believes in diet control
History of any allergy: Not significant
Activity: Severe impairment in daily routine activity, fatigue on exertion
Cognition: No cognitive impairment
Rest and sleep: Decreased sleep
Self-perception: Patient is aware about his disease condition
Coping stress: Good coping strategy
Environmental History
Housing Pattern: Pucca house and well ventilated
Waste /Excreta disposal:Closed, use of dustbins and dumping
Drinking Water Supply: Tap water
Environmental Sanitation: Adequate
Physical examination
Mental Status: Conscious, oriented to time, place and person
Body Development: Weak
Height and Posture: 5 ft 5” Straight and erect posture
Weight: 75kgs
Hygienic condition: Fair
Vital Signs: B P 160/90mmhg, Temp 990F, Respiration 18 breaths /min, Pulse 80/min
Skin: Normal texture but looks shiny, pitting type edema on feet. Skin color is pale.
Head: Hair clean no tangles & pediculosis. Head is normal in shape no deformity noticed.
Table 3
Eyes
|
Eye Brows |
Symmetrical |
|
Eye Lashes |
Normal in position |
|
Eye lids |
Edematous |
|
Conjunctiva |
Pale |
|
Pupils |
Normal size reacting to light |
|
Vision |
Normal |
Table 5
Mouth
|
Lips: |
Bluish (cyanosis) and dry |
|
Tongue: |
Dry |
|
Gums: |
Normal with no any bleeding and gingivitis |
|
Teeth |
No missing teeth but caries present. |
Table 6
Laboratory investigations
Signs & symptoms
Table 8
Neurological
Table 9
Integumentary
|
According to book |
According to patient |
|
Dry,flaky and shiny skin |
Present |
|
Thin & brittle nails |
Absent |
|
Thin hair |
Absent |
Table 10
Cardiovascular
|
According to book |
According to patient |
|
Hypertension |
Present |
|
Pitting edema |
Present |
|
Periorbital edema |
Present |
Table 11
Respiratory or pulmonary
|
According to book |
According to patient |
|
Tachypnea |
Present |
|
Shortness of breath/shallow breath |
Present |
|
Acetone breath smell |
Present |
|
Kussmaul type respiration |
Present |
Table 12
Gastro intestinal
|
According to book |
According to patient |
|
Anorexia, nausea and vomiting |
Present |
|
Metallic taste |
Absent |
Table 14
Genito urinary
|
According to book |
According to patient |
|
Changes in urine output |
Present |
|
Infertility |
Absent |
|
Testicular Atrophy |
Absent |
Table 15
Musculoskeletal system
|
According to book |
According to patient |
|
Muscle cramps |
Present |
|
Bone pain |
Absent |
|
Loss of muscle strength |
Present |
|
Fractures |
Absent |
|
Joint pain |
Present |
Table 16
Complications
|
According to the Book |
According to patient |
|
Hyperkalemia |
Present |
|
Anemia |
Present |
|
Hypertension |
Present |
|
Pericarditis |
Absent |
|
Pericardial effusion &tamponade |
Absent |
|
Bone disease |
Absent |
Table 17
Drug Chart
Table 18
Summary of patients daily progress report
Table 19
Nursing process
Table 0
Table 20
Wholly compensatory system
|
Nurses Action |
Patient had uncontrollable high blood pressure, So I administered diuretics as prescribed. |
Patients action is limited |
|
|
Maintained intake output chart of my patient, checked vital signs. |
|
Table 21
Partially compensatory system
Table 22
Supportive education system
Systemic physical examination
CNS: Patient conscious, oriented and responding to verbal commands.GCS 15/15 E4V5M6
Cardio vascular system: Pulse: Normal rate and rhythm(85b/min).1S2: ++ and no murmurb. B.P: 160/90 mmHg
Respiratory system: Respiratory rate 20b/min, B/L air entry Normal, No crepts/wheeze.
Gastrointestinal system: P/A soft, Non tender with active bowel sounds, slightly distended & having anorexia.
Genitourinary system: Oliguria. Urine is pale yellowish in color& not catheterized.
Musculoskeletal system: Normal range of motion. Absence of any congenital abnormality. Muscle cramps present. Muscle tone is strong and no muscle atrophy. Pitting edema in feet. Reflexes normal.
Motor functions: Motor function is normal and normal cranial function.
Integumentary system (skin): Normal skin texture. Skin color pale.
Sensory function: Normal sensations to temperature, pain, touch etc.
Reflexes: Biceps reflex: Normal, Triceps reflex: Normal, Patellar reflex: Normal, Achilles reflex:, Normal, Deep tendon reflex: Normal
Definition
Chronic kidney disease or chronic renal disease is a progressive loss of renal function over a period of months or years in which metabolic, fluid and electrolyte balance falls, resulting in uremiaor azotemia. In this the GFR falls below 10% of the normal.1, 2, 3, 4, 5 All individuals with a glomerular filtration rate (GFR)<60ml/min/1.73m2for 3 months are classified as havingchronicrenal disease irrespective of the presence or absence of kidney damage. End-stage renal disease (ESRD) occurs when GFR is less than 15ml/min/m2.
Causes
Heredity
Glomerular dysfunction
Cardiovascular disease or cardiovascular risk factors such as Hypertension
Poly cystic kidney disease, Glomerular Nephritis, Urinary tract obstruction, Bladder Tumor, Urethral obstruction, Hypertensive nephrosclerosis.
Diabetic nephropathy
Multi-system disease with potential for kidney involvement
Nephrotoxic drugs
Diagnostic Evaluation
History taking, physical assessment,Urine analysis, Blood chemistry, KFT, LFT, serology, ECG, USG, bone marrow aspiration.
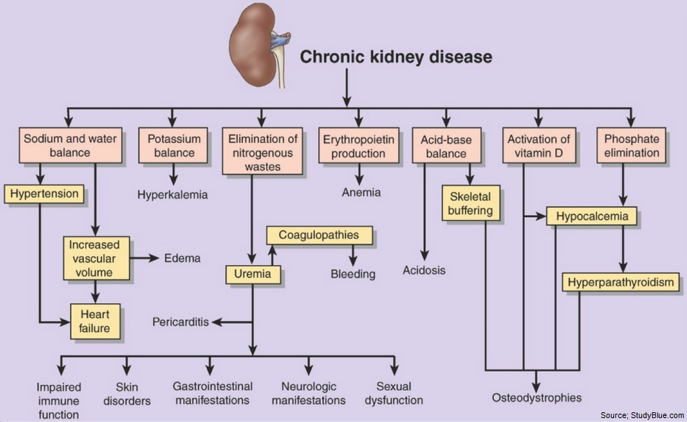
Pathophysiology
Approximately 1 million nephrons are present in each kidney, which contributes to the total GFR. In the case of renal disease regardless of the etiology the nephron has an innate ability to maintain GFR, despite progressive destruction of nephron by hyper filtration and compensatory hypertrophy.6, 7, 8, 9, 10
This nephron adaptability allows for continued normal clearance of plasma solutes. Plasma levels of substances i.e. urea & creatinine starts to increase only if total GFR has decreased to 50%, when the renal reserve has been exhausted. The plasma creatinine value will approx. double with 50% reduction in GFR.
In end-stage renal failure or uremia more than 85% loss of nephron occurs, less than 10% of normal GFR, BUN& serum creatinine at high levels. Anemia, azotemia, metabolic acidosis & urine-specific gravity are fixed at 1.010 oliguria & symptoms of renal failure appears. It is at this Stage where most of the patient face much difficulty in carrying out basic activities of daily living because of the cumulative effect and extent of the symptoms.
Medical Management
Nursing diagnosis
Impaired nutritional status less than body requirements related to anorexia, nausea & vomiting.
Activity intolerance related to fatigue, anemia and dialysis.
Excess fluid volume related to decreased urine output and retention of other waste products.
Headache related to increased B.P(hypertension).
Deficient knowledge regarding disease and treatment.
Application of Nursig Theory
I have selected Orem’s Nursing System theory for application of nursing process on my patient with CKD-ESRD. The focus of Orem’s theory is to enhance patient’s ability for self-care. Three systems exist within this model: The Wholly Compensatory in which the nurse provides the total care; The Partially Compensatory in which the patient and nurse share responsibility of care; Supportive educative system in which patient has the primary responsibility for personal health, with the nurse acting as a consultant.
Discharge teachings/health education
Advised him to Limit the intake of protein rich foods such as kidney, brains, meat extracts etc.
Advised him to take Low potassium diet & Low salt is also encouraged.
Educated to adopt the treatment regimen.
Advised him to get plenty of rest and get more sleep at night.
Advised him to move around and bend his legs to avoid getting blood clots due to rest for a long period of time.
Advised him to keep record of hi daily weights.
Instructed to report hospital if any complication arises.
Advised for regular checkup of BP and blood sugar.
Advised the patient for maintenance hemodialysis.
Assisted him to develop effective coping in day to day life.
Educated regarding renal transplant and its misconceptions.
Instructed the patient to maintain hygiene.
Advised for regular follow up services.
Adherence to dietary restrictions and prescribed medications.
Conclusion
Patients condition (general condition) was fair, GCS 15/15,but had ineffective coping strategies,he was very much worried about his condition & renal transplant. He was not satisfied about the treatment received. Doctors have planned to discharge him till they arrange a donor for kidney.
During case study, health education was provided to patient, checked his vital signs. Monitored blood pressure at regular intervals. Maintained intake output chart. Administered medications as prescribed. Educated the patient and his family regarding maintenance hemodialysis. Advised the patient to come for regular follow- up.