Introduction
The disease process undergoes through four stages.
The premorbid stage
In this stage the person shows social mal-adjustment, social withdrawal, antagonist thoughts, and behavior, it also includes shyness and withdrawal.
The prodromal stage
In this stage the client shows signs and symptoms which can determine either the onset or fully developed disease.
This stage can begin with slight change in premorbid functioning to full devastating disease.
This stage can range from few weeks to years. This stage is accompanied by functioning impairment and symptoms such as anxiety, sleep disturbance, fatigue, poor concentration, depressed mood.4
Active /Acute schizophrenia
This is main and active phase of disorder in which psychotic symptoms are present.
Residual stage
Schizophrenia is characterized by periods of remission and exacerbation. This phase comes after acute phase of illness. In this the symptoms of acute phase are either absent or not prominent.5
Clinical Features
Bleulers 4 As
Table 1
Schizophrenic mind contains the positive and the negative symptoms:
Presenting chief complaints
xx year old female, Divorced 8 yrs back ,9 yrs history of mental illness with 3 days exacerbation of
History of present illness
Duration: 3 days
Mode of onset: Insidious
Course: Fluctuating
Intensity: Increasing
Precipitating Factors: Attending religious ceremony.
3 days back ,patient was in her usual state of health when her family members noticed that her symptoms were worsening. She refused to take medications and on being persuade to do so, she refused and that I will not take medicine ‘You don’t believe me, I am possessed with a jinn that will get transferred’.
Family history:
Table 3
No. of family members: 07 (Seven), there are children of her brother and her son too.
Personal History
History
Full term normal vaginal delivery, No history of maternal infections, birth defect, cyanosis, jaundice. Normal cry at birth.
Child hood history
Primary caregiver: Mother
Feeding: Breastfed.
Developmental milestones: Normal
Behavioral & emotional Problems: Nil.
-
Illness during childhood: Met with an accident with no significant cause.
Educational history: Illiterate never went to school.
Play history: Not good.
Emotional problems during adolescence: Not significant.
Puberty: 14 yrs old with the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics.
Marital History: Married in 2003, divorced in 2009 because of her mental illness.
Pre-morbid personality: Excessively concerned with cleanliness. Frequent washing of clothes and utensils.
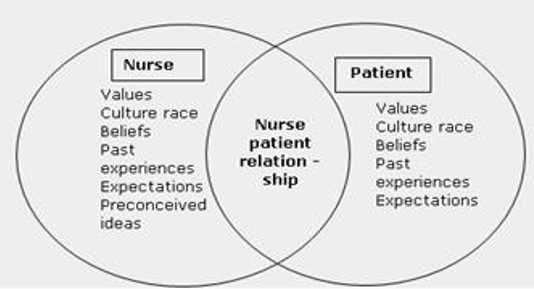
Application of interpersonal relations theory
Basic elements:
The patient
The nurse
The interaction between them
The kind of nurse each person becomes makes a substantial difference in what each client will learn as she or he is nursed throughout his or her experience with illness
Fostering personality development in the direction of maturity is a function of nursing and nursing education; it requires the use of principles and methods that permit and guide the process of grappling with everyday interpersonal problems or difficulties.
Nursing can take as its unique focus the reactions of clients to the circumstances of their illnesses or health problems.
Since illness provides opportunity for learning and growth, nursing can assist clients to gain intellectual and interpersonal competencies, beyond those that they have at the point of illness, by gearing the nursing practices to evolving such competencies through nurse-client interactions6
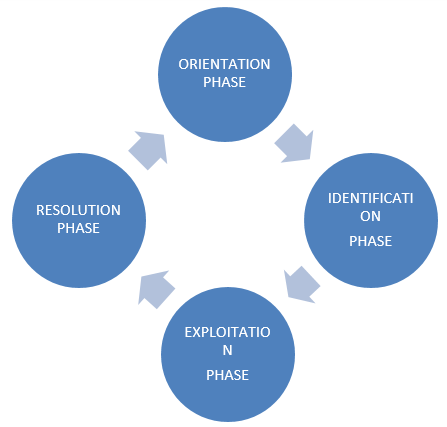
Relationships have four phases
Table 4
Table 5
Influenced Psychobiological Experiences
Within personalities, there are needs, frustrations, conflicts, and anxieties that are influential
Every human has basic needs and goals exerting tensions within the relationship
Nurse’s own self-understanding helps nurse to respond to these tensions and coping mechanisms
Nurse guides patient towards healing; tension and anxiety are converted into purposeful action as the result of the therapeutic relationship7
Nursing care plan according to interpersonal model which will increase interpersonal relation ship and by which patients tension and anxiety gets reduced8
Conclusion
The application of nursing care as per the specific theoritical framework which improves the quality of nursing care. In paplaus theory the healthy nurse patient relationship enhances the quality of care while caring for the client. Focusing on different areas while caring for the client through different stages of relationship can help the client to solve different problems.