- Visibility 25 Views
- Downloads 2 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.ijpns.2022.012
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Effect of structured teaching programme on knowledge regarding modified partograph among auxiliary nurse midwives in selected community health centers
- Author Details:
-
Thounaojam Bidyani Devi *
Background of The Study
Today in public health, maternal mortality remains one of the major problems especially in developing countries where maternal mortality is estimated to be 100 times higher than in developed countries.
The development of the partograph provided health professionals with a pictorial overview of the labour to allow early identification and diagnosis of the pathological labour. The first obstetrician to provide a realistic tool for the study of individual labours was Emanuel Friedman. In 1954, Friedman introduced the concept of a partogram by graphically depicting the dilation of the cervix during labour. In his study of 100 primigravidae at term, cervical dilatation was determined by frequent rectal examinations. For reproducibility, the examination was carried out at the peak of the contraction and for uniformity, measurements were recorded in centimetres. A simple, but effective chart was devised whereby square graph paper was used, with 10 divisions representing the cervical dilatation. The measurements were recorded and joined to the previous measurement in a straight line. The slope of each line was determined in terms of centimetres of dilatation per hour. Friedman’s explanation divided the first stage of labour into two parts: firstly, the latent phase which extends over 8–10 h and up to 3 cm dilatation; secondly, the active phase, characterized by acceleration from 3 to 10 cm, at the end of which is a decelerative phase. The major criticism of the development of this curve was the fact that no exclusions were made for malpresentations, malpositions or multiple pregnancies. Similarly, women receiving oxytocin infusions, caudal analgesia and/or operative delivery were included. The current partogram is designed to monitor not only the progress of labour, but also the condition of the mother and the fetus during labour.[1], [2], [3], [4], [5]
In late sixties and early seventies several extensive studies were carried out and it was inferred that labour in primipara and multipara behaved differently and deviation from normal could be diagnosed by the use of the partograph. Over last two decades several developed and developing countries have used partograph pragmatically in variety of different setting and have found it to be inexpensive and effective tool for diagnosing labour outcome. An estimated 358,000 women died due to complications developed during pregnancy and childbirth.
WHO, UNICEF and UNFPA produced a report with statistics gathered. The world average per 100,000 was 400, the average for developed regions were 20, and for developing regions 440. Seventy-five percent of maternal deaths occur during childbirth and postpartum period.
The studies above revealed that partogram is a valuable tool in the improvement of labour outcome and among these skilled attendances during pregnancy, labour and delivery have been identified as the most important factor in the reduction of maternal mortality and morbidity. Keeping the above facts in view, the investigator took up the task to assess the knowledge of ANM’s regarding partogram so that making aware of the standard protocol on partogram can fill missing links and knowledge gaps. [6], [7], [8], [9], [10], [11]
Statement of the problem
A pre experimental study to evaluate the effect of structured teaching programme on knowledge regarding modified partograph among auxiliary nurse midwives in selected community health centers of Bhopal division, M.P.
Objectives of The Study
Assess the pre test knowledge on modified partograph among auxiliary nurse midwives.
Assess the post test knowledge on modified partograph among auxiliary nurse midwives.
Compare the pre and post test knowledge on modified partograph among auxiliary nurse midwives.
Associate the pre test level of knowledge on modified partograph among auxiliary nurse midwives with their selected demographic variables.
Research hypotheses
H1:- There is significant difference between pre-test and post-test knowledge score on modified partograph among auxiliary nurse midwives at 0.05 level of significance.
H2:- There is significant association of pre test knowledge score on modified partograph with selected demographic variables of auxiliary nurse midwives at 0.05 level of significance.
Materials and Methods
Research approach
An experimental research approach was selected to evaluate the effect of structured teaching programme on knowledge regarding modified partograph among auxiliary nurse midwives.
Research design
In present study pre-experimental one group pre-test, post-test design was used to observe the effect of structured teaching programe among Auxiliary Nurse Midwives regarding modified partograph.
Research setting
The study is being conducted in Community Health Center Gandhinagar, Bhopal division.
Variables
Independent variable
Structured teaching programme on modified partograph was the independent variable in the study.
Dependent variable
Knowledge of auxiliary nurse midwives on modified partograph was the dependent variable in the study.
Population
In this study population is Auxiliary Nurse Midwives working in Community Health Center, Gandhinagar, Bhopal division.
Sample
In this study sample is a part of population which consists of auxiliary nurse midwives who fulfills the inclusive criteria.
Sampling technique
Auxiliary nurse midwives who fulfilled the inclusion criteria and working in the selected community health centers are selected as sample by non-probability convenient sampling technique because of the availability of subjects according to the inclusive sampling criteria within the limited time period.
Criteria for sample selection
Inclusive criteria
Auxiliary nurse midwives who are willing to participate in study.
Auxiliary nurse midwives who are available at the time of data collection.
Auxiliary nurse midwives who has at least 1 year of experience.
Exclusive criteria
Auxiliary nurse midwives who had special exposure or in-service training on partograph.
Development of tool
On the basis of the objectives of the study and review of literature, tools are developed. The tool for the study are:
Structured teaching programme on modified partograph.
Close ended questionnaire to assess the knowledge regarding modified partograph among Auxiliary Nurse Midwives.
Description of tool
Structured teaching plan
Structured teaching plan was organized for enhancing knowledge among auxiliary nurse midwives consisting of introduction, definition, purpose, labour, principles of assessing partograph, components of partograph, process of partograph recording, advantages of partograph and conclusion.
Closed ended questionnaire
It was prepared to assess the knowledge of Auxiliary Nurse Midwives regarding modified partograph. The closed ended questionnaire consists of 2 parts.
Part A: It consists of structured questionnaire to collect demographic data. It contains eleven items to obtain information regarding age, marital status, basic qualification, professional qualification, clinical experience, experience in labour room, practice of partograph in labour room, previous information and its source, supply of partograph, use of partograph and their confidence in using partograph.
Part B: It consists of structured questionnaire to assess knowledge on modified partograph. The structured questionnaires regarding modified partograph consist of thirty multiple choice questions under aspects such as introduction, definition, purposes, stages of labour, principles, charting of partograph.
Data analysis and interpretation
Section-I: Distribution of auxiliary nurse midwives according to their demographic variable.
|
Characteristics |
Respondents |
|
|
Frequency |
Percentage |
|
|
Age in years |
|
|
|
a. 20-25 years |
6 |
10 |
|
b. 26-30 years |
12 |
20 |
|
c. 31-35 years |
19 |
31.667 |
|
d. > 35 years |
23 |
38.333 |
|
Marital status |
|
|
|
a. Single |
7 |
11.667 |
|
b. Married |
53 |
88.333 |
|
c. Divorced |
0 |
0 |
|
d. Separated |
0 |
0 |
|
Basic qualification |
|
|
|
a. High School |
40 |
66.667 |
|
b. Higher secondary |
12 |
20 |
|
c. Graduate |
6 |
10 |
|
d. Post graduate and above |
2 |
3.333 |
|
Professional qualification |
|
|
|
a. 18 months revised Auxiliary nurse |
51 |
85 |
|
b. midwives MPHW(F) |
|
|
|
c. 2 years Auxiliary nurse midwives (ANM) |
9 |
15 |
|
Total years of clinical experience |
|
|
|
a. 1-4 years |
15 |
25 |
|
b. 5-6 years |
4 |
6.667 |
|
c. 7-8 years |
6 |
10 |
|
d. 9 years and above |
35 |
58.333 |
|
Year of experience in labour room |
|
|
|
a. 1-3 years |
22 |
36.667 |
|
b. 4-5 years |
4 |
6.667 |
|
c. 6-7 years |
9 |
15 |
|
d. 7 years and above |
25 |
41.667 |
|
Whether the partograph is being routinely used in labour room |
|
|
|
a. Always |
15 |
25 |
|
b. Almost always |
15 |
25 |
|
c. Seldom |
20 |
33.333 |
|
d. Never |
10 |
16.667 |
|
Previous source of information |
|
|
|
a. No |
52 |
86.667 |
|
b. Yes |
8 |
13.333 |
|
If yes |
|
|
|
a. During training |
52 |
86.667 |
|
b. In service education attended |
|
|
|
c. Internet |
|
|
|
d. All of the above |
|
|
|
Whether the partograph sheet is being supplied by the concerning department |
|
|
|
a. Yes |
28 |
46.667 |
|
b. Sometimes |
14 |
23.333 |
|
c. No |
18 |
30 |
|
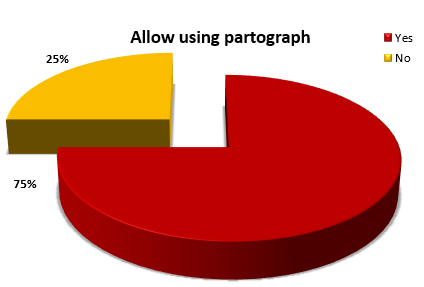
Whether medical officers / gynaecologists allow to use partograph |
|
|
|
a. Yes |
45 |
75 |
|
b. No |
15 |
25 |
|
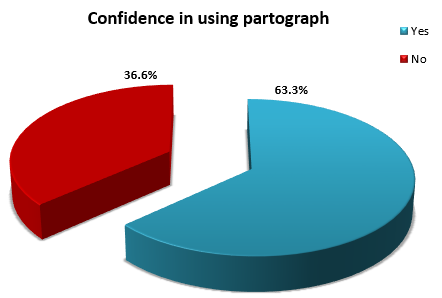
Are you confident in using partograph |
|
|
|
a. Yes |
38 |
63.333 |
|
b. No |
22 |
36.667 |
Section-II Assessment of pre test knowledge score of auxiliary nurse midwives regarding modified partograph
|
Grade |
Pre test |
|||
|
Frequency |
Percentage |
Mean |
S.D. |
|
|
Inadequate |
31 |
51.7 |
10.65 |
3.82 |
|
Satisfactory |
29 |
48.3 |
||
|
Adequate |
0 |
0 |

The data in the figure reveals that in the pre test knowledge scores of auxiliary nurse midwives on modified partograph more than half of samples (51.67%) had inadequate knowledge where (48.3%) had satisfactory knowledge.
Section-III: Assessment of post test knowledge score of auxiliary nurse midwives regarding modified partograph
|
Grade |
Post test |
|||
|
Frequency |
Percentage |
Mean |
S.D. |
|
|
Inadequate |
0 |
0 |
19.17 |
3.92 |
|
Satisfactory |
36 |
60 |
||
|
Adequate |
24 |
40 |

The data in the figure depicts that in the post test knowledge scores of auxiliary nurse midwives on modified partograph more than half of the samples (60%) had satisfactory knowledge where (40%) had adequate knowledge.
Section IV: Comparison between the pre and post test knowledge score of auxiliary nurse midwives regarding modified partograph.
|
Group |
Mean |
Mean difference |
Mean percentage |
Standard deviation |
‘t’ value |
|
Pre test |
10.65 |
8.52 |
35.5 |
3.82 |
12 S**** |
|
Post test |
19.17 |
63.9 |
3.92 |
The data in the table depicts that the pre test mean score of knowledge assessed by structured knowledge questionnaire was 10.65 with SD of +/- 3.82. In the post test mean score was 19.17 with SD of +/-3.92. This indicates that there is significant difference between pre-test and post-test knowledge score on modified partograph among auxiliary nurse midwives at 0.05 level of significance hence research hypothesis H1 is accepted.

The data in the figure depicts that in the pre test knowledge scores of auxiliary nurse midwives on modified partograph more than half of the samples (51.7%) had inadequate knowledge where (48%) had satisfactory knowledge. Whereas in post test knowledge scores of auxiliary nurse midwives on modified partograph more than half of the samples (60%) had satisfactory knowledge where (40%) had adequate knowledge.
Line diagram was drawn to compare the pre test and post test knowledge scores of Auxialiary Nurse Midwives regarding modified partograph shows that the lowest pre test score values were between 4-6 obtained by 17% Auxialiary Nurse Midwives and highest score values were between 19-21 obtained by only 3% Auxialiary Nurse Midwives. However, during the post test, the lowest score values were between 10-12 obtained by 5% Auxialiary Nurse Midwives and highest score values were between 25-27 obtained by only 11% Auxialiary Nurse Midwives. Further, during the pre test the highest percentage (35%) Auxialiary Nurse Midwives score between 10-12, whereas during post test the highest percentage (27%) Auxialiary Nurse Midwives scored between.[12], [13], [14]
Further, the mean and median plotted for pre and post test scores shows that during pre test mean and median values were 10.65 and 10, whereas during post test it was 19.17 and 19 respectively revealing that the difference of approximately 9 scores. Hence, it can be interpretated that the STP was effective in improving the knowledge of Auxialiary Nurse Midwives regarding modified partograph.
O-give curve showing the comparison between pre test and post test cumulative percentage of knowledge scores on modified partograph among Auxiliary Nurse Midwives shows that the O-give curve values on post test score was higher than the pre test scores.
In the pre test 25th percentile score was 2.8, whereas it was 5.5 for the post test that the difference of 2.7. The 50th percentile score for pre test was 3.5, which was 6.2 for the post test revealing the difference of 2.7. The 75th percentile score of pre test was 4.2, which was 7.5 for the post test revealing the difference of 3.3. It reveals that difference between pre and post test curve is highest at 75th percentile revealing the effect of STP regarding modified partograph among Auxiliary Nurse Midwives
Section V: Association of pre test knowledge score of auxiliary nurse midwives with their selected demographic variables.
|
Demographic variables |
Inadequate 0-10 |
Satisfactory 11-20 |
df |
Chi-square value |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
No. |
% |
No. |
% |
|||
|
Age in years |
|
|
|
|
|
0.028 |
|
20-25 years |
3 |
5 |
3 |
5 |
|
N.S. |
|
26-30 years |
6 |
10 |
6 |
10 |
3 |
|
|
31-35 years |
10 |
16.7 |
9 |
15 |
|
|
|
> 35 years |
12 |
20 |
11 |
18.3 |
|
|
|
Marital status |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Single |
3 |
5 |
4 |
6.7 |
1 |
0.232 |
|
Married |
28 |
46.7 |
25 |
41.7 |
|
N.S. |
|
Basic qualification |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
High School |
22 |
36.7 |
18 |
30 |
|
|
|
Higher secondary |
7 |
11.7 |
5 |
8.3 |
3 |
3.202 |
|
Graduate |
2 |
3.3 |
4 |
6.7 |
|
N.S. |
|
Post graduate and above |
0 |
0 |
2 |
3.3 |
|
|
|
Professional qualification |
|
|
|
|
1 |
1.337 |
|
18 months revised Auxiliary nurse midwives MPHW (F). |
28 |
46.7 |
23 |
38.3 |
|
N.S. |
|
2 years Auxiliary nurse midwives (ANM). |
3 |
5 |
6 |
10 |
|
|
|
Total years of clinical experience |
|
|
|
|
3 |
4.558 N.S. |
|
1-4 years |
7 |
11.7 |
8 |
13.3 |
|
|
|
5-6 years |
4 |
6.7 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
7-8 years |
2 |
3.3 |
4 |
6.7 |
|
|
|
9 years and above |
18 |
30 |
17 |
28.3 |
|
|
|
Year of experience in labour room |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1-3 years |
11 |
18.3 |
11 |
18.3 |
|
|
|
4-5 years |
2 |
3.3 |
2 |
3.3 |
|
|
|
6-7 years |
4 |
6.7 |
5 |
8.3 |
3 |
0.39 |
|
7 years and above |
14 |
23.3 |
11 |
18.3 |
|
N.S. |
|
Whether the partograph is being routinely used in labour room |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Always |
9 |
15 |
6 |
10 |
3 |
1.253 |
|
Almost always |
7 |
11.7 |
8 |
13.3 |
|
N.S. |
|
Seldom |
11 |
18.3 |
9 |
15 |
|
|
|
Never |
4 |
6.7 |
6 |
10 |
|
|
|
Previous source of information |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
No |
5 |
8.3 |
3 |
5 |
1 |
0.466 |
|
Yes |
26 |
43.3 |
26 |
43.3 |
|
N.S. |
|
Whether the partograph sheet is being supplied by the concerning department |
|
|
|
|
|
3.338 N.S. |
|
Yes |
18 |
30 |
10 |
16.7 |
|
|
|
Sometimes |
6 |
10 |
8 |
13.3 |
|
|
|
No |
7 |
11.7 |
11 |
18.3 |
|
|
|
Whether medical officers / gynaecologists allow to use partograph Yes |
27 |
45 |
18 |
30 |
1 |
4.869 S* |
|
No |
4 |
6.7 |
11 |
18.3 |
|
|
|
Are you confident in using partograph |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
22 |
36.7 |
16 |
26.7 |
1 |
1.654 |
|
No |
9 |
15 |
13 |
21.7 |
|
N.S. |
The data in the table depicts that the association of pre test knowledge score on modified partograph with their selected demographic variables. In relation to age, marital status, basic qualification, professional qualification, clinical experience, experience in labour room, practice of partograph in labour room, previous information and its source, supply of partograph and their confidence in using partograph with modified partograph, the chi square value obtained 0.028, 0.232, 3.202, 1.337, 4.558, 0.39, 1.253, 0.466, 3.338 and 1.654 respectively. It is identified that there is no significant association of pre test knowledge score on modified partograph in relation to age, marital status, basic qualification, professional qualification, clinical experience, experience in labour room, practice of partograph in labour room, previous information and its source, supply of partograph and their confidence in using partograph of auxiliary nurse midwives except the allowance of using partograph by medical officers / gynaecologists with chi square value 4.869 at 0.05 level of significance.[15], [16]
Conclusion
On the basis of the findings of the study, the following conclusions were drawn:
Highest percentage of Auxiliary Nurse Midwives (38.3%) were in the age group >35 years and (88.3%) were married. Highest percentage of Auxiliary Nurse Midwives (66.6%) were having high school basic qualification and (85%) were from 18 months revised auxiliary nurse midwives MPHW (F). Highest percentage of Auxiliary Nurse Midwives (58.3%) had 9 years and above total clinical experience, (41.6%) had 7 and above years of experience in labour room and (33.3%) Auxiliary Nurse Midwives had seldom used partograph in labour room. Highest percentage of Auxiliary Nurse Midwives (86.6%) had previous source of information during training. Highest percentage of Auxiliary Nurse Midwives (46.6%) agreed that partograph sheet is been supplied by the concerning department, (75%) agreed that use of partograph is allowed by medical officers / gynaecologists where (63.3%) are confident in using partograph.
Prior to the administration of structured teaching plan the highest percentage of Auxiliary Nurse Midwives (51.7%) had inadequate knowledge whereas highest percentage of Auxiliary Nurse Midwives (60%) had satisfactory knowledge after administration of structured teaching plan.
The mean pre test knowledge score was 10.65 whereas the mean post test knowledge score was 19.17. The post test scores proved that the structured teaching programme given by the investigator, helped auxiliary nurse midwives to improve their knowledge.
There is no significant association of pre test knowledge score on modified partograph with their selected demographic variables of Auxiliary Nurse Midwives except the allowance of using partograph by medical officers / gynaecologists with chi square value 4.869 at 0.05 level of significance.
Source of Funding
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- S Anuchithra. Partogram or partograph: Nurses of India. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- P Amudha. Assessment of effectiveness of structured teaching programme on breast self examination for early detection of breast cancer:. Nightingale Nurs Times 2009. [Google Scholar]
- S Aruna. Astudy to assess the effectiveness of the structured teaching programme on self-care management of patients with diabetes mellitus in Chennai:. Indian J Holistic Nurs 2006. [Google Scholar]
- J K Basu, E J Buchmann, D Basu. A study to evaluate role of a second stage partogram in predicting the outcome of normal labour: Australian and New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology. Obstetr Gynecol 2007. [Google Scholar]
- G Dangal. Preventing prolonged labor by using partograph: . Internet J Gynecol Obstet 2005. [Google Scholar]
- M H Devi. A study to evaluate the effectiveness of self instructional module on selected cardiac emergency drugs for the nursing personnel working in the critical care unit in selected hospitals of Kolkata:. Asian J Cardiovascular Nurs 2009. [Google Scholar]
- I Diarra, S Camara, M K Maiga. Assessment of the use of partogram at the district maternity hospital of commune II in Bamako area: . US National Libr Med National Institutes of Health 2008. [Google Scholar]
- J S Dohbit. A survey study to evaluate the knowledge, attitude and practice of the labour partograph among birth attendants of the primary and secondary care level hospitals of Yaounde-Cameroon:. Geneva-yaonde Cooperation Scholarship 2006. [Google Scholar]
- M Fahdhy, V Chongsuvivatwong. Evaluation of World Health Organisation partograph implementation: Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology. Available 2004. [Google Scholar]
- A O Fawole, K I Hunyinbo, D A Adekanle. Knowledge and utilization of the partograph among obstetric care givers in south west Nigeria. Afr J Reprod Health 2008. [Google Scholar]
- A O Fawole, D A Adekanle, K I Hunyinbo. Knowledge and use of the partograph among healthcare personnel at the peripheral maternity centers in Nigeria. Nigeria J Clin Pract 2010. [Google Scholar]
- S Kumawat, D Martin, M Joshi. Effect of structured teaching program on foot care for type II diabetic patients:. Indian J Nurs Stud 2009. [Google Scholar]
- V Leanza, G Leanza, S Monte. The didactic protocol on the management of both labour and birth: the partogram: Minerva Ginecologica. Minerva Ginecol 2009. [Google Scholar]
- C E Lennox, B E Kwast, T M M Farley. A study on the impact of breech labour management using the WHO partograph on fetal and maternal outcomes of labor in South East Asia:. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1997. [Google Scholar]
- M Lentic. Could the central part of the partograph, the cervicograph be improved. J Maternal Fetal and Neonatal Med 2006. [Google Scholar]
- S Madhuri. A study to assess the effect of planned health teaching on knowledge regarding preventive and control measure related to malaria among people in selected urban slum area of Pune city:. Indian J Holistic Nurs 2006. [Google Scholar]
